MRdataset : unified interface to various neuroimaging datasets#

Description#
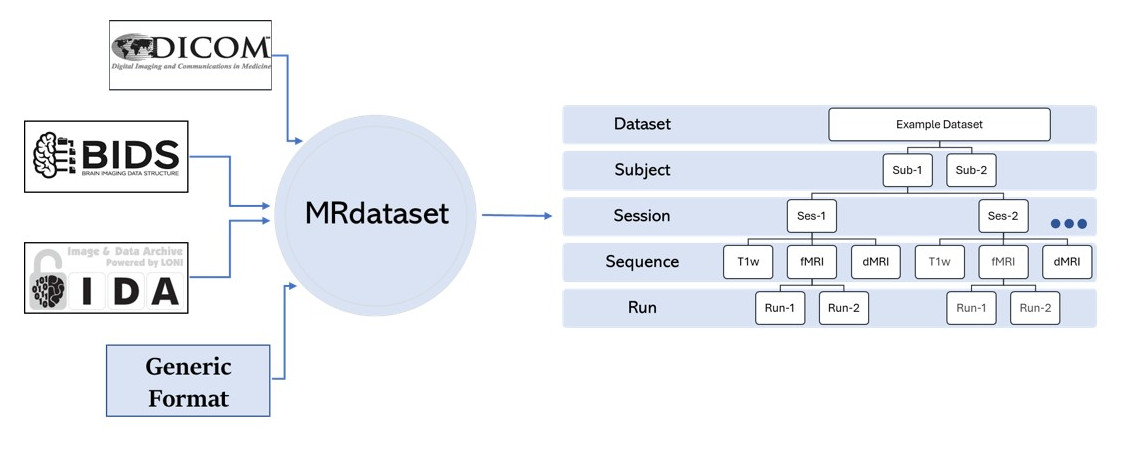
Provides a unified interface for horizontal and vertical traversal of various neuroimaging datasets (DICOM) and any other generic format etc.
Ensures that the DICOM files are valid imaging DICOMs and provides the option to skip phantoms, localizer, head scouts etc.
Provides flexibility to ignore automatically generated derived scans such as MoCo series, Single-band references, perfusion weighted scans.
Verifies if each DICOM slice belongs to the same scan volume and, then subsequently organizes all scans are hierarchical fashion (Subject > Session > Sequence > Run)
Identifies sequences acquired within the same session, which is especially useful for associating field maps with their corresponding functional (EPI) scans.
Tutorial: Please refer to the Jupyter Notebook tutorial.
Documentation: https://open-minds-lab.github.io/MRdataset/
API usage#
To use MRdataset in a project -
import MRdataset
The most important method is import_dataset. The dataset type
such as dicom or bids can be specified using the ds_format argument.
from MRdataset import import_dataset
Given a valid folder path to a dataset of MR images (e.g. DICOM images), it creates a dataset.
data_folder = '/home/user/datasets/XYZ'
dataset = import_dataset(data_source=data_folder,
ds_format='dicom')
By default, the import_dataset expects a DICOM dataset. However, this can
be changed using ds_format argument. For example, use ds_format='bids' for
importing a BIDS dataset.
We follow a hierarchical structure in our dataset as shown above. And we provide methods for
accessing each of these elements. These access-methods are traverse_horizontal
and traverse_vertical2. For example, we can traverse through all the subjects for a given sequence
using traverse_horizontal method.
seq_name = '3D_T2_FLAIR'
for subject, session, run, sequence in dicom_dataset.traverse_horizontal(seq_name):
print(f"Subject: {subject},\nSession: {session},\nRun: {run},\nSequence: {sequence}")
Similarly, we can traverse through all the sequences/modality for a given subject using traverse_vertical2 method. It is helpful for retrieving epi and corresponding fieldmaps for a given subject. Let's see an example.
seq_id1 = 'me_fMRI'
seq_id2 = 'me_FieldMap_GRE'
for subject, session, run1, run2, seq1, seq2 in dicom_dataset.traverse_vertical2(seq_id1, seq_id2):
print(seq1)
print(seq2)
break
Finally, save_mr_dataset and load_mr_dataset can be used to save and load a
dataset. For example, to save a dataset
from MRdataset import save_mr_dataset
save_mr_dataset(dataset, '/home/user/datasets/xyz.mrds.pkl')
Similarly, to load a dataset
from MRdataset import load_mr_dataset
dataset = load_mr_dataset('/home/user/datasets/xyz.mrds.pkl')
Note that the dataset is saved as a pickle file with an extension .mrds.pkl.
Command line usage#
MRdataset can be used on the command line interface. For a DICOM dataset
mrds --data-source /path/to/dataset --format dicom
For a BIDS dataset
mrds --data-source /path/to/dataset --format bids
- cli()
The following arguments are supported:
- -d, --data-sourcestr
directory containing downloaded dataset with dicom files, supports nested hierarchies
- --configstr
path to config file
- -o, --output-dirstr
specify the directory where the dataset would be saved.
- -f, --formatstr
choose type of dataset, expected one of [dicom|bids]
- -n, --namestr
provide an identifier/name for dataset. If not provided, the name of the dataset will be a random string e.g. '54321'
- --is-partialbool
flag dataset as a partial dataset. The flag is useful while reading a dataset in chunks e.g. when the dataset is too large to fit in memory. If the dataset is complete, the flag should not be set.
Examples
mrds -d /path/to/my/data/ --format dicom --name abcd_baseline --config mri-config.json --output-dir /path/to/my/output/dir/